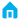
The error of gears is an important indicator for evaluating the quality of gear processing. It is usually divided into relative errors and absolute errors, which have a direct impact on the transmission accuracy, stability and service life of gears.
Relative error and absolute error of gears:
- The absolute error refers to the difference between the actual size and the theoretical size of the gear. It is a specific quantity, usually in millimeters (mm) or microns (μm). Absolute errors include pitch error, tooth shape error, tooth direction error and ring gear radial runout error, etc.
- The relative error is the ratio of the absolute error to a specific size of the gear (usually the theoretical size), usually expressed as a percentage. Relative error reflects the severity of the error and is an important parameter for measuring machining accuracy.
The influence of absolute error and relative error on the smoothness of gear transmission:
1.The influence of tooth pitch error:
- Absolute error: The greater the absolute value of the tooth pitch error, the more obvious the gear will jump during the transmission process, resulting in uneven transmission.
- Relative error: When the relative value of the tooth pitch error is large, it indicates that the inaccuracy of the tooth pitch is serious relative to the gear size, which will affect the meshing quality of the gear and reduce the smoothness of the transmission
2.The influence of tooth form error:
- Absolute error: A large absolute value of tooth profile error will cause impact and noise when the gear meshes, increasing instability in the transmission process.
- Relative error: A large relative error means that the deviation of the tooth profile is larger than the tooth profile size, which will affect the meshing performance of the gear and reduce the smoothness of the transmission.
3.The influence of tooth direction error:
- Absolute error: A large absolute value of the tooth direction error will cause the gear to generate axial force during transmission, causing axial vibration and affecting the smoothness of the transmission.
- Relative error: A large relative error indicates that the tooth direction deviation is significant relative to the gear length, which will lead to instability of the gear during transmission.
4.The influence of ring gear radial runout error:
- Absolute error: The absolute value of the radial runout error of the ring gear is large, which will cause the radial runout of the gear during rotation, resulting in unstable transmission.
- Relative error: A large relative error means that the radial runout of the ring gear is larger than the gear diameter, which will affect the positioning accuracy and transmission stability of the gear.
To sum up, the absolute error and relative error of gears will have a negative impact on the smoothness of gear transmission. The size of the absolute error is directly related to the maximum deviation that may occur during the transmission process, while the relative error reflects the severity of these deviations relative to the gear size. In order to ensure the smoothness and reliability of gear transmission, both errors need to be strictly controlled, and the errors can be reduced by improving processing accuracy and inspection standards, thereby improving the overall performance of gear transmission.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!